Відмінності між версіями «Embedded system»
Лілія (обговорення • внесок) |
Ivan (обговорення • внесок) |
||
| (не показані 8 проміжних версій ще одного учасника) | |||
| Рядок 1: | Рядок 1: | ||
| + | [[Файл:Ukraine.gif|link=вбудована система|50px]] | ||
| + | [[Файл:Flagros.gif|link=встраиваемая система|50px]] | ||
[[Файл:Embedded-system.jpg|обрамити|праворуч|Embedded system]] | [[Файл:Embedded-system.jpg|обрамити|праворуч|Embedded system]] | ||
| − | An embedded system (укр. [[вбудована система]]) is a computer system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal computer (PC), is designed to be flexible and to meet a wide range of end-user needs. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. | + | An '''embedded system''' (укр. [[вбудована система]]) is a computer system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal computer (PC), is designed to be flexible and to meet a wide range of end-user needs. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. |
| − | + | '' | |
| − | Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e CPUs with integrated memory and/or peripheral interfaces) but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also still common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) used may be types ranging from rather general purpose to very specialised in certain class of computations, or even custom designed for the application at hand. A common standard class of dedicated processors is the digital signal processor (DSP). | + | Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e CPUs with integrated memory and/or peripheral interfaces) but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also still common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) used may be types ranging from rather general purpose to very specialised in certain class of computations, or even custom designed for the application at hand. A common standard class of dedicated processors is the digital signal processor (DSP).'' |
The key characteristic, however, is being dedicated to handle a particular task. Since the embedded system is dedicated to specific tasks, design engineers can optimize it to reduce the size and cost of the product and increase the reliability and performance. Some embedded systems are mass-produced, benefiting from economies of scale. | The key characteristic, however, is being dedicated to handle a particular task. Since the embedded system is dedicated to specific tasks, design engineers can optimize it to reduce the size and cost of the product and increase the reliability and performance. Some embedded systems are mass-produced, benefiting from economies of scale. | ||
Physically, embedded systems range from portable devices such as digital watches and MP3 players, to large stationary installations like traffic lights, factory controllers, and largely complex systems like hybrid vehicles, MRI, and avionics. Complexity varies from low, with a single microcontroller chip, to very high with multiple units, peripherals and networks mounted inside a large chassis or enclosure | Physically, embedded systems range from portable devices such as digital watches and MP3 players, to large stationary installations like traffic lights, factory controllers, and largely complex systems like hybrid vehicles, MRI, and avionics. Complexity varies from low, with a single microcontroller chip, to very high with multiple units, peripherals and networks mounted inside a large chassis or enclosure | ||
| + | ==Hardware for Embedded Systems== | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microcontroller Microcontrollers] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_electronics Digital Electronics] | ||
| + | *[http://www.zums.ac.ir/files/research/site/ebooks/it-programming/digital-systems-design.pdf Digital System Design] | ||
| + | *[http://users.ece.cmu.edu/~koopman/des_s99/communications/ Embedded Communication] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AS-Interface Sensors, Actuators and Interfacing] | ||
| + | ==Software for Embedded Systems== | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_C C for Embedded Systems] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_software Embedded Software Development] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_operating_system Embedded Operating Systems] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphical_user_interface_builder GUI development] | ||
| + | *[http://www.embedded.com/print/4407007 Multicore Programming] | ||
| + | *[http://www.comtrade.com/software-engineering/embedded-systems-development/professional-testing-of-embedded-systems-software/ Testing] | ||
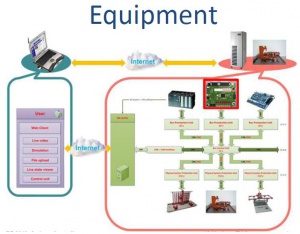
| + | ==Equipment== | ||
| + | [[Файл:Equipment.JPG|праворуч|300px]] | ||
| + | *Set up for DSP, Embedded SW, Embedded OS, digital systems, μcontrollers, embedded communication, CAD/CAM/CAE: (exemplary, actual implementation may differ) | ||
| + | **Pandaboard ES: Single Board Computer with 1.2GHz dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 OMAP4460, 1GB RAM, WiFi, Bluetooth, USB + case; | ||
| + | **Cables: HDMI to DVI-D, U.FL-RPSMA; | ||
| + | **BWZ3-RA: antenna 2400MHz; | ||
| + | **Sandisk SDHC card 16GB; | ||
| + | **Logitech C615 Full HD-webcam; | ||
| + | **Nexys™3 Spartan-6 FPGA Board; | ||
| + | **Basic microcontroller board | ||
| + | **Zigbee USB Module; | ||
| + | |||
==Video== | ==Video== | ||
{{#ev:youtube|tj3GmD2cXHw}} | {{#ev:youtube|tj3GmD2cXHw}} | ||
| + | [[Категорія:Tempus/Dictionary]] | ||
Поточна версія на 11:48, 13 травня 2014
An embedded system (укр. вбудована система) is a computer system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal computer (PC), is designed to be flexible and to meet a wide range of end-user needs. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e CPUs with integrated memory and/or peripheral interfaces) but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also still common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) used may be types ranging from rather general purpose to very specialised in certain class of computations, or even custom designed for the application at hand. A common standard class of dedicated processors is the digital signal processor (DSP).
The key characteristic, however, is being dedicated to handle a particular task. Since the embedded system is dedicated to specific tasks, design engineers can optimize it to reduce the size and cost of the product and increase the reliability and performance. Some embedded systems are mass-produced, benefiting from economies of scale.
Physically, embedded systems range from portable devices such as digital watches and MP3 players, to large stationary installations like traffic lights, factory controllers, and largely complex systems like hybrid vehicles, MRI, and avionics. Complexity varies from low, with a single microcontroller chip, to very high with multiple units, peripherals and networks mounted inside a large chassis or enclosure
Hardware for Embedded Systems
- Microcontrollers
- Digital Electronics
- Digital System Design
- Embedded Communication
- Sensors, Actuators and Interfacing
Software for Embedded Systems
- C for Embedded Systems
- Embedded Software Development
- Embedded Operating Systems
- GUI development
- Multicore Programming
- Testing
Equipment
- Set up for DSP, Embedded SW, Embedded OS, digital systems, μcontrollers, embedded communication, CAD/CAM/CAE: (exemplary, actual implementation may differ)
- Pandaboard ES: Single Board Computer with 1.2GHz dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 OMAP4460, 1GB RAM, WiFi, Bluetooth, USB + case;
- Cables: HDMI to DVI-D, U.FL-RPSMA;
- BWZ3-RA: antenna 2400MHz;
- Sandisk SDHC card 16GB;
- Logitech C615 Full HD-webcam;
- Nexys™3 Spartan-6 FPGA Board;
- Basic microcontroller board
- Zigbee USB Module;